
Custom Restaurant Menu Printing
Custom restaurant menu printing in London helps attract customers, boost sa...
-


Custom restaurant menu printing in London helps attract customers, boost sa...

RV AC repairing services, you can ensure that your air conditioning system...

Digital marketing continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological adva...

Find the best lawyer for car accident claims. Learn how to choose an expert...

Many small businesses are at a disadvantage competing with big brands in th...
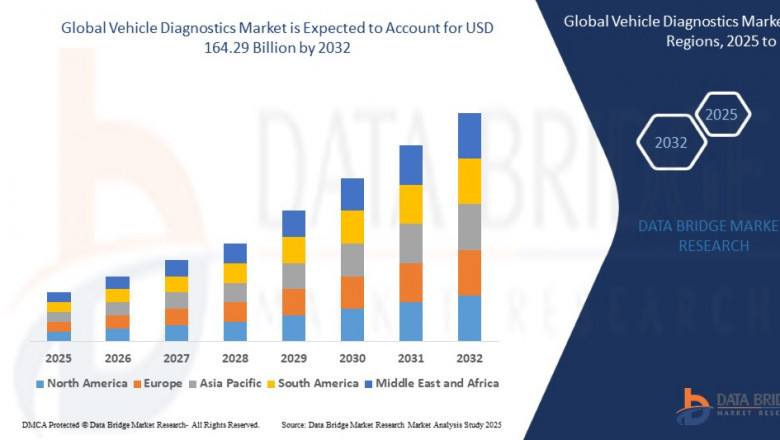
Vehicle Diagnostics Market, Vehicle Diagnostics Market Trends, Vehicle...
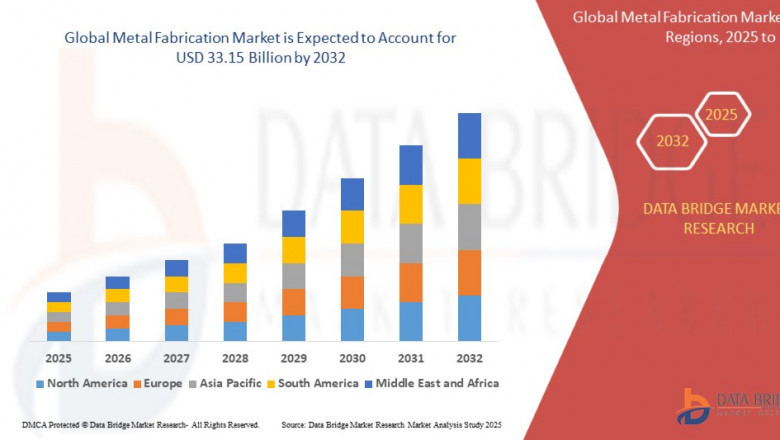
Metal Fabrication Market, Metal Fabrication Market Trends, Metal Fabric...
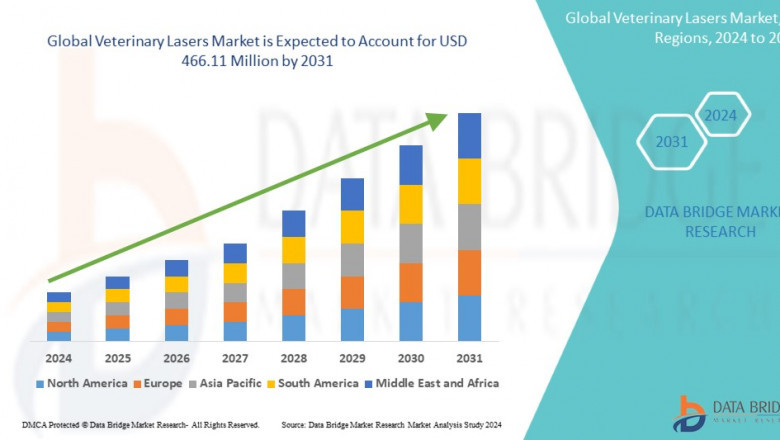
Veterinary Lasers Market, Veterinary Lasers Market Trends, Veterinary L...

