views
Dental Bonding Cementing
Understanding the difference between temporary vs. permanent dental cement is essential for anyone undergoing restorative dental procedures such as crowns, bridges, or veneers. Dental Bonding Cementing acts as an adhesive, bonding prosthetic materials to natural teeth. While both types serve the same fundamental purpose—securing restorations in place—they differ in composition, strength, and intended duration of use. Dentists choose between the two based on treatment stages, patient needs, and long-term goals. Knowing what type is used in your procedure can help you better care for your dental work and recognize when something may go wrong.
Purpose and Use of Temporary Dental Cement:
Temporary dental cement is designed for short-term use and plays a critical role in procedures that require flexibility, monitoring, or adjustments. It is most often used between dental visits or when the final restoration isn’t ready yet.
Key uses of temporary cement include:
-
Securing provisional crowns or bridges until permanent ones are placed
-
Testing bite alignment or aesthetics before final cementation
-
Allowing healing time after root canal therapy or surgical procedures
-
Easy removal of temporary restorations for follow-up work
-
Emergency repairs for dislodged crowns or fillings
Temporary cements are formulated for easy application and removal. They offer moderate retention but can weaken over time, making it vital to follow your dentist’s timeline for permanent placement.
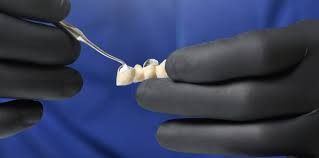
Characteristics of Permanent Dental Cement:
Permanent dental cement is intended to hold dental restorations in place for many years, offering superior strength and long-lasting adhesion. Once applied, it’s extremely difficult to remove without professional tools and technique.
Core features of permanent cement include:
-
Durability and resistance to chewing forces and temperature changes
-
Strong chemical bonding to enamel, dentin, and restoration material
-
Moisture resistance to prevent breakdown over time
-
Biocompatibility to ensure comfort and minimize irritation
-
Aesthetic blending with tooth structure in cosmetic applications
Dentists carefully prepare both the tooth surface and the restoration before applying permanent cement to ensure a secure fit and optimal longevity.
Material Differences Between the Two:
While both types of cement may look similar in appearance, their formulations differ to suit their specific purpose. The chemistry affects not only how they perform but also how they are handled during procedures.
Common distinctions in composition:
-
Temporary cements often contain zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE) or non-eugenol alternatives that provide mild antibacterial properties and soothing effects
-
Permanent cements include resin-based, glass ionomer, or hybrid resin-modified formulas designed for enhanced bonding and strength
-
Setting times for temporary cements are faster and less rigid to allow easier adjustments
-
Permanent cements may require light or dual curing for stronger polymerization and a tight seal
These chemical differences are crucial in determining how long a cement will last and how easily a restoration can be removed if needed.
When Dentists Choose One Over the Other?
Choosing between temporary vs. permanent dental cement isn’t random—it depends on clinical context and the patient’s specific situation. Dentists assess multiple factors before deciding which type of cement will deliver the best results.
Situations where temporary cement is preferred:
-
During trial placement of crowns, veneers, or bridges
-
For healing or observation after surgical procedures
-
In orthodontics where adjustments may be needed
-
As a temporary solution in emergencies or travel
Situations requiring permanent cement:
-
Final crown and bridge placement
-
Long-term veneers or inlays/onlays
-
Implant-supported restorations
-
Post-root canal permanent sealing
Each case is evaluated for durability, aesthetics, and function before cementation.
Patient Tips for Each Cement Type:
Whether you have a temporary or permanent restoration, proper care is essential. Understanding how to maintain the integrity of your Dental Bonding Cementing Treatment helps avoid complications and prolongs the life of your dental work.
For temporary dental cement:
-
Avoid sticky or hard foods that may dislodge the temporary piece
-
Call your dentist if the restoration becomes loose or falls off
-
Be gentle with brushing and flossing around the temporary area
-
Do not delay your follow-up visit for permanent placement
For permanent dental cement:
-
Practice daily oral hygiene to protect surrounding teeth and gums
-
Visit your dentist regularly to monitor the bond and restoration
-
Avoid chewing on non-food objects that could stress the cement
-
Watch for sensitivity or discomfort which could indicate leakage
Understanding the role of both types of dental cement ensures you can take the right actions to protect your oral health and maintain the effectiveness of your treatment.



Comments
0 comment