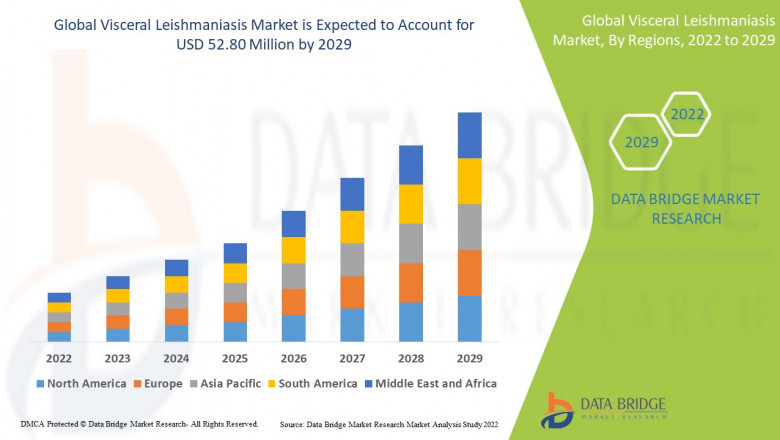
Visceral Leishmaniasis Market Size, Share, Trends, Dema...
Data Bridge Market Research analyses a growth rate in the g global visceral...
-


Data Bridge Market Research analyses a growth rate in the g global visceral...
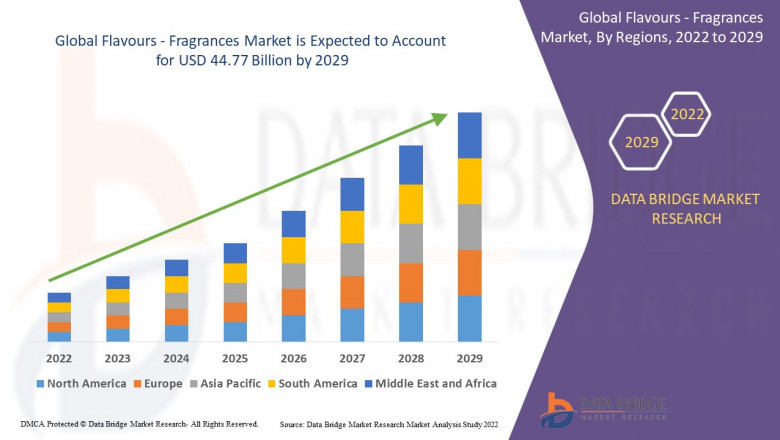
Global flavours-fragrances market size was valued at USD 34.36 billion in 2...

Learning how to drive is an essential skill that opens up opportunities for...
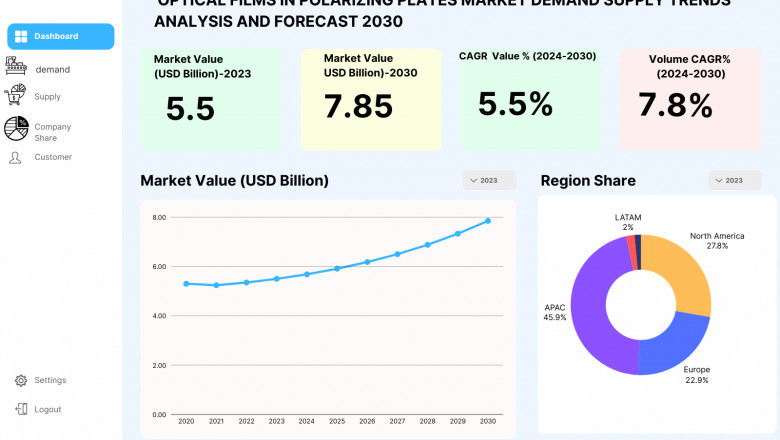
The Optical Films in Polarizing Plates Market is projected to grow from USD...
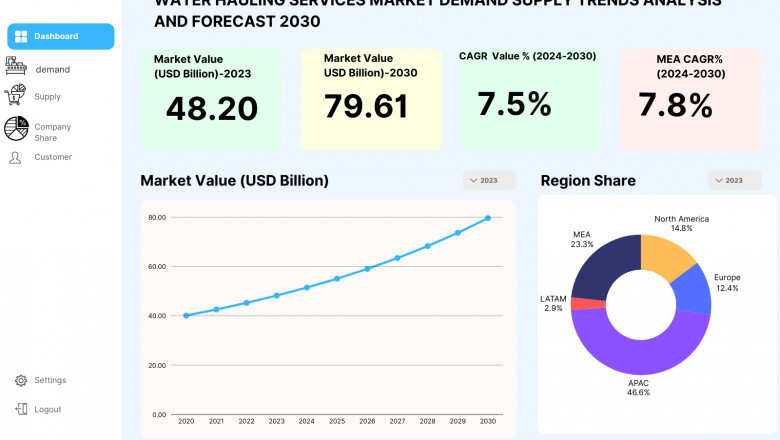
The water hauling services market is expanding due to increased industrial...

Jewelry represents love, connection, and style, not just decoration. Totwoo...
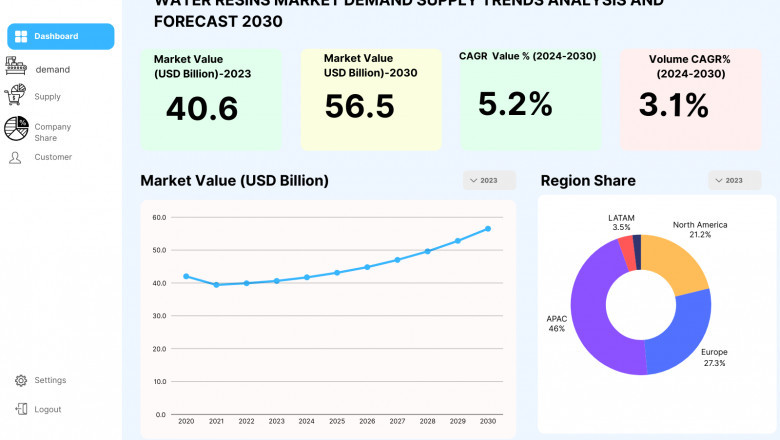
The water-based resins market is growing rapidly due to increasing demand f...

At ICAD Joinery, we believe that a well-designed kitchen is more than just...

